|
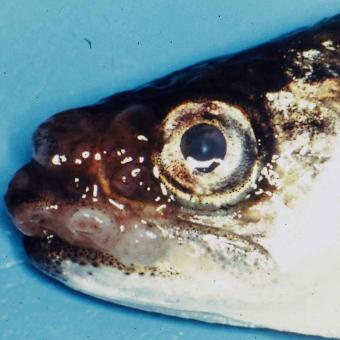
Oncorhynchus masou virus (also known as OMV), is a viral disease of salmonids, particularly coho and masu salmon, and rainbow trout. OMV is taxonomically classified as a Herpes virus and primarily affects salmonids in Japan, but has been reported from as far afield as Kuwait. When identifying OMV infections, initial signs may include anorexia, darkening of the body, skin ulcers and lethargy; these are all signs of systemic disease. The mortality rate in juvenile fish is very high, and surviving fish regularly develop cutaneous tumors, particularly on the head and jaw. The virus is spread through both diseased fish and asymptomatic carriers, via excretions or direct fish-to-fish contact. It is possible that the disease can be spread also on the surface of eggs during spawning. OMV is not a human health threat. |
|
Distribution:
Hosts: Salmon and trout
Japan and other locations
|
|
Detection Method:
cell culture - unspecified Target tissue:
Skin |